Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the PostgreSQL CREATE TABLE AS statement to create a new table from the result set of a query.
Introduction to the PostgreSQL CREATE TABLE statement
The CREATE TABLE AS statement creates a new table and fills it with the data returned by a query. The following shows the syntax of the CREATE TABLE AS statement:
CREATE TABLE new_table_name
AS query;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this syntax:
- First, specify the new table name after the
CREATE TABLEclause. - Second, provide a query whose result set is added to the new table after the
ASkeyword.
The TEMPORARY or TEMP keyword allows you to create a temporary table:
CREATE TEMP TABLE new_table_name
AS query; Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The UNLOGGED keyword allows the new table to be created as an unlogged table:
CREATE UNLOGGED TABLE new_table_name
AS query;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The columns of the new table will have the names and data types associated with the output columns of the SELECT clause.
If you want the table columns to have different names, you can specify the new table columns after the new table name:
CREATE TABLE new_table_name ( column_name_list)
AS query;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)If you want to avoid an error by creating a new table that already exists, you can use the IF NOT EXISTS option as follows:
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS new_table_name
AS query;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)PostgreSQL CREATE TABLE AS statement examples
We will use the film and film_category table from the sample database for the demonstration.
The following example uses the CREATE TABLE AS statement to create a new table that contains the films whose category is 1:
CREATE TABLE action_film
AS
SELECT
film_id,
title,
release_year,
length,
rating
FROM
film
INNER JOIN film_category USING (film_id)
WHERE
category_id = 1;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)To verify the table creation, you can query data from the action_film table:
SELECT * FROM action_film
ORDER BY title;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)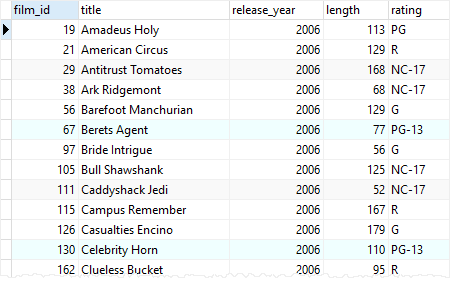
To check the structure of the action_film, you can use the following command in the psql tool:
\d action_film;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)It returns the following output:
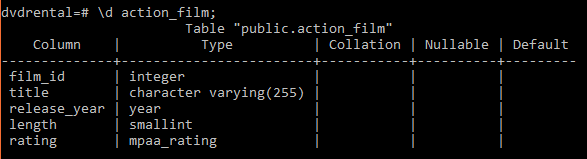
As clearly shown in the output, the names and data types of the action_film table are derived from the columns of the SELECT clause.
If the SELECT clause contains expressions, it is a good practice to override the columns, for example:
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS film_rating (rating, film_count)
AS
SELECT
rating,
COUNT (film_id)
FROM
film
GROUP BY
rating;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)This example statement created a new table film_rating and filled it with the summary data from the film table. It explicitly specified the column names for the new table instead of using the column names from the SELECT clause.
To check the structure of the film_rating table, you use the following command in psql tool:
\d film_ratingCode language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The following is the output:
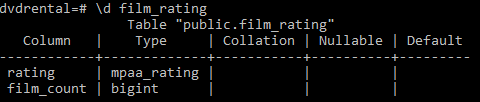
Note that the CREATE TABLE AS statement is similar to the SELECT INTO statement, but the CREATE TABLE AS statement is preferred because it is not confused with other uses of the SELECT INTO syntax in PL/pgSQL. In addition, the CREATE TABLE AS statement provides a superset of the functionality offered by the SELECT INTO statement.
Summary
- Use the PostgreSQL
CREATE TABLE ASstatement to create a new table from the result of a query.